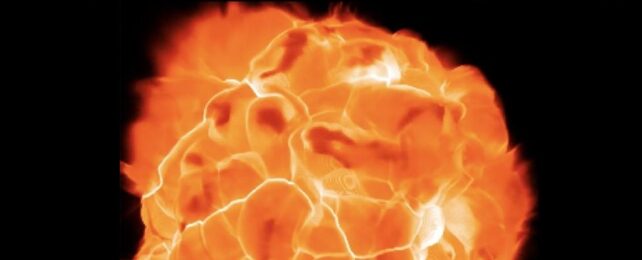
Betel-gurz or Beetle-juice has been a favourite among amateur astronomers for many years. However you pronounce it, its unexpected dimming draws even more attention to this red supergiant variable star in Orion.
It has a few cycles of variability. One of them occurs over a 2,170 day period, five times longer than its normal pulsation period. A paper has just been published that suggests a companion star of 1.17 solar masses could be the cause.
It would need an orbit about 2.43 times the radius of Betelgeuse and it might just lead to the modulation of dust in the region that causes the variations we see.
One of the brightest stars in the sky, Betelgeuse is a red supergiant found situated prominently at the upper left of the constellation Orion. It represents the shoulder of the hunter although some translations suggest it refers to 'the armpit of the giant!'

It's one of the largest stars visible to the unaided eye with a radius about 1,000 times the Sun. At a distance of 642 light years away, its brightness in our sky tells us it must be giving out about 100,000 times more light than the Sun.
Over the last five years it's been getting special attention due to its unexpected dimming.
The dimming occurred toward the end of 2019 and then returned to normal in the first half of 2020. It's generally accepted that the dimming was caused by a dust cloud in the event that has now been dubbed 'The Great Dimming.'
As a well-known variable star, the light curve of Betelgeuse displays a Long Secondary Period (LSP) of approximately 2100 days. It's not unusual for stars in the Red Giant Branch of the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram and can range from a few hundred days to thousands.
To date though, the mechanism behind the LSP is unknown but it certainly does seem to be a secondary cycle to a shorter one. Interestingly the duration of the LSP seems to be generally in the region of a few tens of times slower than the stars radial pulsation.
It's the nature of this longer term variability in Betelgeuse that is the focus of a new paper published by Jared A. Goldberg and his team. A greater understanding will lead to a greater clarity of Betelgeuse's evolutionary stage and ultimately to its death.
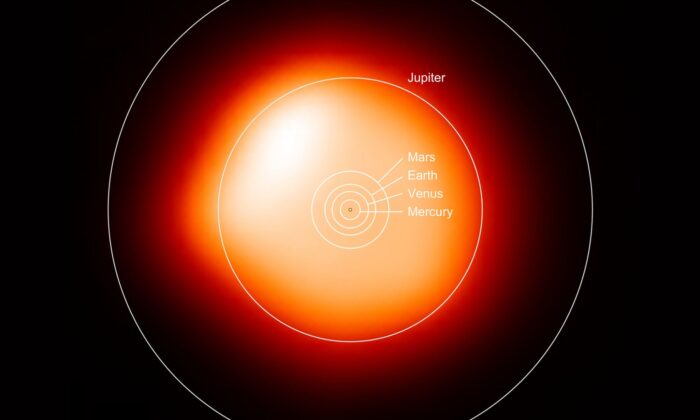
One solution points to it simply being the result of the pulsation of the outer layers. If this were the case then it means Betelgeuse is larger than expected and would be further along its evolution branch and that a supernova explosion may be imminent within the next few hundred years!
An exciting prospect for the stargazers among us.

Interestingly though, the team conclude that the most likely explanation for the long term variability of Betelgeuse is a low mass companion star, named Ori B (Betelgeuse bears the alternative name Alpha Orionis.)
It is possible that this binary star could be modulating the dust surrounding the system and when the companion is in transit, the dust leads to a reduction in brightness. If Ori B were to be confirmed, it would have a significant impact on our evolutionary understanding of Betelgeuse.
It is expected to go supernova soon but this is largely because observed variations led to the conclusion it was close. Instead, Ori B being the cause means we may have some time to wait after all.
This article was originally published by Universe Today. Read the original article.