The very early Universe was a dark place. It was packed with light-blocking hydrogen and not much else.
Only when the first stars switched on and began illuminating their surroundings with UV radiation did light begin its reign. That occurred during the Epoch of Reionization.
But before the Universe became well-lit, a specific and mysterious type of light pierced the darkness: Lyman-alpha emissions.
Even though the early Universe was too dark for light to travel through the opaque gas that dominated it, astronomers have still detected some Lyman-alpha lines prior to the lights coming on in the Epoch of Reionization.
Where did it come from? That's been a significant unanswered question that many have pondered.

Lyman-alpha emissions occur in the UV range and come from hydrogen atoms as their electrons transition to a specific energy state. Lyman-alpha spectral lines are part of what astronomers call the Lyman-alpha forest.
The forest is a series of absorption lines stemming from the hydrogen in distant astronomical objects. As their light passes through gas clouds with different redshifts, it creates the forest of Lyman-alpha lines.
"Providing an explanation for the surprising detection of Lyman-alpha in these early galaxies is a major challenge for extragalactic studies," the authors of some new research write.
The research is published in Nature Astronomy and may have found the answer. Its title is "Deciphering Lyman-alpha emission deep into the epoch of reionization." The lead author is Callum Witten, a researcher at the Kavli Institute for Cosmology at Cambridge University in the UK.
"One of the most puzzling issues that previous observations presented was the detection of light from hydrogen atoms in the very early Universe, which should have been entirely blocked by the pristine neutral gas that was formed after the Big Bang," Witten said in a press release.
"Many hypotheses have previously been suggested to explain the great escape of this 'inexplicable' emission."
But now there's a new cosmological sheriff in town: the James Webb Space Telescope.

The JWST was built with the ability to peer back to the Universe's early days. That was one of the primary drivers of the entire endeavour.
The JWST's ability to sense the photons released by the stars in the first galaxies early in the Universe's life has opened a new window into the early Universe and is leading us toward answers to many long-standing questions. The JWST has both the sensitivity and the angular resolution to follow ancient light back to its source.
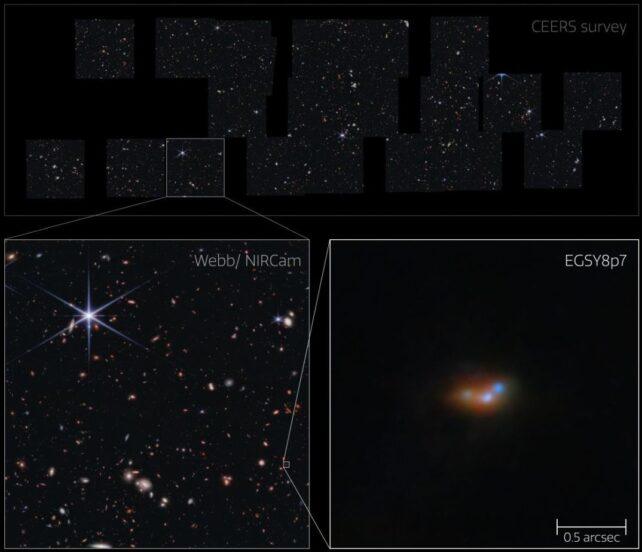
"Here, we take unique advantage of both high-resolution and high-sensitivity images from the James Webb Space Telescope Near Infrared Camera to show that all galaxies in a sample of Lyman-alpha emitters with redshift >7 have close companions," the researchers write in their paper. This is an important point with huge implications.
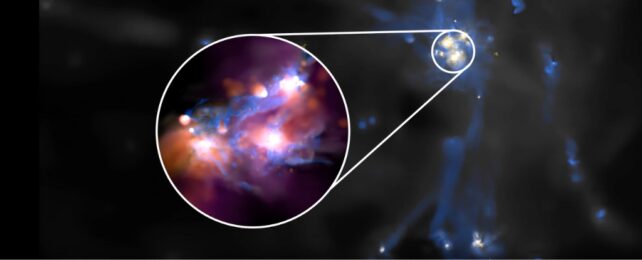
The JWST images of the Lyman-Alpha emitter LAE EGSY8p68 reveal more detail than previous observations with the Hubble Space Telescope. The JWST's resolving power reveals a clump of smaller, dimmer galaxies around the bright galaxies in LAE EGSY8p68 that the HST couldn't see. The region is a much busier, crowded region with lots of active star formation.
"Where Hubble was seeing only a large galaxy, Webb sees a cluster of smaller interacting galaxies, and this revelation has had a huge impact on our understanding of the unexpected hydrogen emission from some of the first galaxies," said study co-author Sergio Martin-Alvarez from Stanford University.
The early galaxies were prodigious star producers and were a rich source of Lyman-alpha emissions. Most of the emissions were blocked by the primordial neutral hydrogen that filled the space between galaxies in the early Universe. What does it tell us that most Lyman-Alpha Emitters (LAEs) are galaxies with close neighbours?
According to the authors, it tells us that galactic mergers and their abundant star formation are behind the Lyman-alpha emissions. A galactic merger simulation produced a mock JWST image that looks remarkably like the actual JWST image of interacting galaxies.

The researchers used simulations of galactic mergers and interactions called Azahar to test their idea. Azahar showed that as stellar mass gathered and stars formed in these early galaxies, two things happened.
The stars emitted Lyman-alpha emissions, and they created bubbles and channels of ionized hydrogen in the light-blocking neutral hydrogen. The bubbles and channels allowed Lyman-alpha emissions through.
This research shows that there were more galactic mergers in the early Universe than we could see before the JWST got going.
Those mergers and interactions and the abundant star formation that they spawned are responsible for both creating the Lyman-alpha emissions and creating a path for them out of the dense, opaque neutral hydrogen that dominated the young Universe.
In a nutshell, the high galactic merger rate in the young Universe is responsible for the mysterious Lyman-alpha emissions.
The researchers aren't done yet. They're planning more detailed observations of galaxies at different stages of merging to develop their idea even more.
This article was originally published by Universe Today. Read the original article.